Introduction
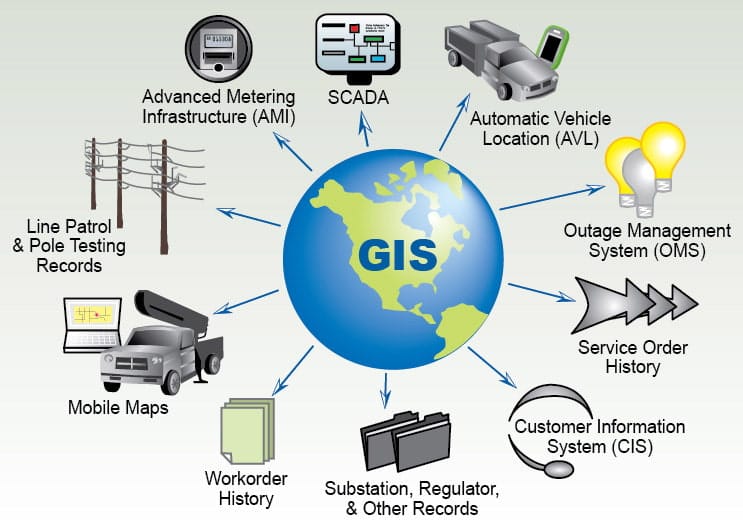
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Geospatial Technology are modern technological tools used for capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and visualizing data that is associated with specific geographic locations. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a computer-based system used to capture, store, analyse, manage, and visualize spatial (location-based) data or data that is referenced to specific locations on the Earth. It is designed to handle spatial data and associated attributes. It allows the combination of “where” (location) with “what” (information about that location), making it possible to perform advanced spatial analyses and produce meaningful maps and models. This implies that GIS links geographic (map) data with descriptive (attribute) information, helping decision-makers understand “where things happen” and “why they happen there.”
In simpler terms, GIS helps us answer the following five questions:
- Where is it?
- What is it?
- What is happening around it?
- What patterns or relationships exist?
GIS allows users to integrate various datasets, analyse spatial and non-spatial relationships, and produce maps and models that support informed decision-making. Geospatial technology, on the other hand, encompasses a wider range of tools including GPS, remote sensing, photogrammetry, and spatial analysis software that collectively enable accurate spatial data collection and interpretation. These technologies have revolutionized various sectors including surveying, environmental management, agriculture, disaster management, urban planning, public health, transportation, and infrastructure development. The integration of spatial and attribute data within GIS enables effective decision-making and supports a wide variety of spatial analyses.
Geospatial technology is used as a collective term that refers to a range of tools used to acquire, manipulate, and visualize geographic information. It also mean a broader field that includes all the tools and techniques used to collect, store, analyze, and visualize geographic data. It encompasses several interconnected technologies.
Core Functions of GIS
The major functions of GIS are stated as follows
- Mapping and visualization
- Data collection and management
- Spatial analysis (proximity, overlay, buffer, etc.)
- Modeling and prediction
- Decision support and reporting
GIS is a computer-based system that captures, stores, checks, integrates, manipulates, analyzes, and displays spatial data. It connects location-based data (where things are) with attribute data (what things are).
Conclusion
GIS and Geospatial Technology form the backbone of modern spatial analysis and Earth observation. They integrate diverse datasets, enable advanced modelling, and create powerful visualizations that support evidence-based decisions. As technology advances especially with drones, cloud computing, IoT, and AI geospatial science is becoming even more central to global development, infrastructure planning, environmental sustainability, and smart city initiatives.
Contact Geoinfotech Academy for further understanding on GIS and Geospatial Technology. Do training with us to learn new things at your convenience and expand your horizon. We educate and empower People