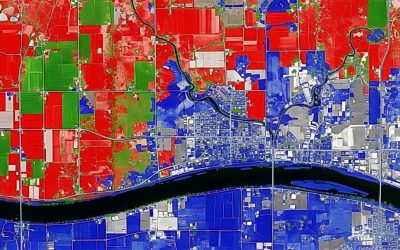
Introduction: Seeing the Unseen
Have you ever wondered how your favorite weather app seems to know exactly when to tell you to grab an umbrella? Or perhaps you’ve seen those incredible, sweeping images of Earth from space, showing everything from vast forests to sprawling cities. How do we get such detailed information about our planet without actually being there?

Deconstructing Remote Sensing – The Basics
To truly understand how remote sensing impacts your life and environment, we first need to take a look under the hood and understand the fundamental principles at play. Think of this as our “Remote Sensing 101” – the essential building blocks.
In simple terms, remote sensing is the process of detecting and measuring the electromagnetic radiation reflected, emitted, or scattered from objects or areas. This crucial data is then analyzed to understand the characteristics of those objects or areas without physically touching them. It’s like being able to study the traffic patterns during rush hour from a satellite image, without needing to be stuck in the gridlock yourself.
The magic of remote sensing happens through a series of key steps. It all begins with a source of electromagnetic energy, which can be natural, like the sun’s radiation illuminating the Earth, or artificial, where the sensor itself emits energy. When this energy reaches the Earth’s surface or atmosphere, it interacts with different features like land, water, buildings, vegetation, and even the air itself. This interaction can involve reflection, absorption, or transmission, and crucially, different materials interact with different types of energy in unique ways.
These interactions are then captured by sensors, which are the “eyes” in the sky, or sometimes on the ground or in the air. These instruments detect and measure the energy that has interacted with the target. Sensors can be mounted on various platforms: satellites, orbiting the Earth to provide a broad view and repeated coverage, vital for monitoring large-scale changes like deforestation or coastal erosion. While less common for broad-area sensing, ground-based sensors can also be used for specialized tasks like monitoring air quality in a specific industrial zone.
During data collection, these sensors record the intensity of the electromagnetic radiation across different wavelengths – think of these as different “colors” of light, including those invisible to our eyes. This raw data is then transmitted to ground stations for subsequent processing. This data processing is where the magic truly unfolds, as the raw data is corrected for distortions, calibrated, and then transformed using specialized software into meaningful information.
We can broadly categorize remote sensing into two main types based on the energy source. Passive Remote Sensing relies on naturally available energy, primarily from the sun, with the sensor detecting the sunlight reflected or emitted by the Earth’s surface. Regular cameras and many satellite imaging systems like Landsat and Sentinel, which provide valuable data for monitoring changes in landscape, are prime examples of passive sensors, operating only when there is natural illumination. In contrast, Active Remote Sensing involves sensors that provide their own source of energy, which is emitted towards the target, and then measure the energy reflected back. Examples include Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging), which sends out microwave pulses and measures the reflected signal, making it particularly useful for mapping flooded areas even under cloud cover, as it can penetrate clouds and vegetation. Similarly, LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses laser pulses to measure distances and create precise 3D models of the Earth’s surface, employed for detailed terrain mapping, studying building heights in urban areas and surveying vegetation structure.
Remote Sensing in Action – Impacting Your Daily Life
One of the most immediate and tangible impacts of remote sensing is in Weather Forecasting & Climate Monitoring. Every time you check your phone for the day’s forecast, or hear a warning about an approaching storm, you’re benefiting directly from remote sensing. Satellites equipped with advanced sensors continuously track atmospheric conditions, cloud formations, and ocean temperatures. This data is crucial for predicting rainfall patterns, issuing warnings for heavy downpours that can lead to flash floods and even for tracking larger systems like tropical depressions. Beyond daily weather, these same systems are vital for long-term climate monitoring, helping scientists understand phenomena like sea-level rise and monitoring changes in regional temperatures.
Remote sensing plays an indispensable role in Urban Planning & Development. Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide planners with up-to-date maps of land use, revealing where new informal settlements are emerging, how urban infrastructure like roads and bridges are expanding, and identifying areas of unmanaged growth. This data helps authorities make informed decisions about resource allocation, infrastructure development, and even waste management strategies. By tracking changes over time, remote sensing aids in creating more sustainable and organized urban environments.
Remote sensing helps farmers monitor crop health, assess irrigation needs, predict yields, and even detect early signs of plant diseases or pest infestations from above. This ‘precision agriculture’ helps optimize farming practices, reduce waste, and ultimately contributes to more stable food prices and a more consistent supply of produce.
When disaster strikes, remote sensing becomes an immediate lifeline in Disaster Management & Emergency Response. For a city prone to seasonal flooding, such as certain low-lying areas after heavy rains, satellite and drone imagery can quickly map inundated areas, assess the extent of damage to infrastructure like homes and roads, and identify safe routes for emergency services to reach affected populations. During emergencies like building collapses or large fires, high-resolution imagery can provide critical situational awareness for first responders, aiding in search and rescue operations and ensuring more effective and targeted relief efforts.
Beyond immediate crises, remote sensing is a silent guardian in Environmental Monitoring & Conservation. It helps track critical environmental issues, such as deforestation in nearby rural areas that contributes to soil erosion, monitoring the health of coastal mangrove ecosystems that protect against storm surges, or assessing the extent of plastic pollution in waterways. By providing regular, consistent data on these environmental indicators, remote sensing empowers environmental agencies and conservation groups to identify problem areas, monitor the effectiveness of environmental policies, and work towards a healthier environment.
Finally, while often overlooked as a remote sensing application, the very foundation of modern Navigation & Mapping relies heavily on satellite technology, which shares principles with remote sensing. Your smartphone’s map apps, ride-sharing services like Uber and Bolt, and the efficiency of delivery services all depend on precise location data provided by global navigation satellite systems (GNSS). These systems, while not ‘sensing’ the environment in the same way as imagery satellites, are part of the broader ecosystem of space-based data.
Remote Sensing and Your Immediate Environment
Remote sensing is crucial for monitoring local green spaces and urban sprawl. Imagine living in a densely populated area. Urban planners and environmental agencies use high-resolution satellite and drone imagery to track the health of nearby parks and recreational areas. Is the vegetation thriving, or showing signs of stress due to pollution or lack of maintenance? Remote sensing can tell us. Furthermore, it provides invaluable data on how city growth – where new buildings are springing up, where informal settlements are expanding, and how effectively master plans are being adhered to. These insights directly influence decisions about where new public facilities are located, where road networks need expansion, or even where basic amenities might be lacking in newly developed areas.
A critical concern for any urban dweller is tracking local air and water quality. While you might not see the sensors directly, remote sensing data contributes to understanding the environmental health of your local area. Satellites can detect the concentration of pollutants like nitrogen dioxide or particulate matter in the atmosphere, helping to identify areas with higher air pollution from traffic congestion or industrial activities. This information can then inform public health advisories or push for cleaner energy sources in specific industrial zones. Similarly, by monitoring coastal waters and lagoons, remote sensing can help identify areas affected by effluent discharge or illegal dumping, contributing to efforts to improve the water quality in our immediate environment.
For a city so vulnerable to flooding, especially during the rainy seasons, remote sensing is a vital tool for flood risk assessment and mitigation. Experts use detailed elevation models created by LiDAR and radar imagery to precisely map flood-prone areas right down to specific streets and compounds. This allows for better urban drainage planning, the identification of critical choke points in canals and drainages that need clearing, and helps authorities issue targeted warnings to residents in areas prone to flooding. By understanding the flow of water and potential inundation zones from above, city planners can make more informed decisions about infrastructure development and emergency preparedness that directly protect your home and community.
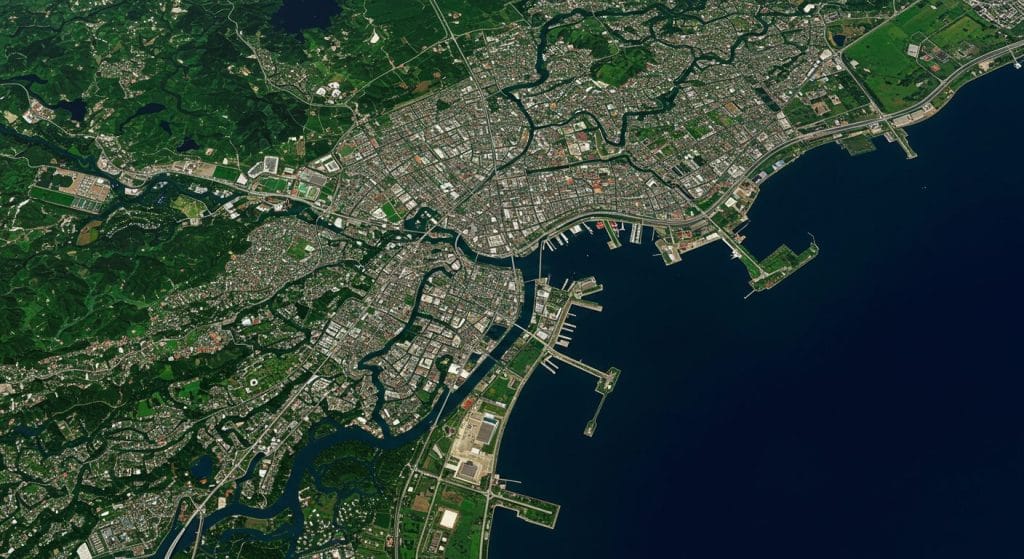

Conclusion: A World Seen from Above
It’s clear that this ‘seeing from a distance’ technology is far more than just pretty satellite images. It’s an indispensable tool that empowers us with knowledge – knowledge to predict, to plan, to protect, and to respond. It helps authorities understand a city’s relentless growth, identify areas vulnerable to flooding, monitor environmental changes that affect our health, and even ensure the efficiency of the food supply that reaches our markets. Remote sensing quietly works behind the scenes, providing the critical intelligence needed to manage a bustling city, making informed decisions that ultimately aim for a more sustainable, resilient, and thriving urban environment.
The next time you check your weather app before heading out, or see a news report about urban development or environmental conservation efforts, take a moment to remember the silent, powerful eyes in the sky making it all possible. Remote sensing isn’t just a scientific concept; it’s an active, transformative force shaping the world we live in, one data point at a time. As technology continues to advance, imagine how much more we’ll be able to ‘see’ and understand, and how this will continue to evolve and impact our lives in the future.
Share Your Thoughts
What aspect of remote sensing surprised you the most? How do you think this technology could further benefit your community or address specific challenges? Share your insights and questions in the comments below