Landscape Planning and Design using GIS
Landscape Planning and Design using GIS
Landscape planning is the development and implementation of strategies, policies, and plans in both urban and rural settings for the benefit of present and future generations. Landscape Architectural context requires Landscape architects work to in all contexts and scales, from global to local, and on all sorts of development, advising on or managing plans for change that may have an impact on the landscape. They examine and resolve environmental, economic, and social opportunities and limitations pertinent to landscape interest areas, and take these into account when addressing a landscape’s potential and capacity to accommodate change.

GIS plays a key role during the process of developing landscape projects and plans. GIS is regarded as a spatial context for natural science intelligence synthesis in landscape architecture and design. GIS is defined specifically as a tool for determining the parametric location of territories (morphometric, hydrological, lithological, soil, biocoenosis, process, etc.) in the geographical diversity of landscapes.
GIS, like other tools such as microscopes and telescopes, can help landscape architects see what the naked eye cannot see by realistically modeling past, present, and future conditions or superimposing information for the study. GIS should be seen as an external cognitive instrument that helps and mediates the learning of design information. GIS aids in that it can handle the ‘same types of design knowledge regarding components of landscape architectonic composition in a more accurate, systematic, clear, and quantifiable manner. GIS mediates in the sense that it influences what and how aspects of the composition can be understood, allowing design researchers to generate “new types of design knowledge” through advanced spatial analysis and the ability to link or integrate other information layers, fields of science, and data sources.
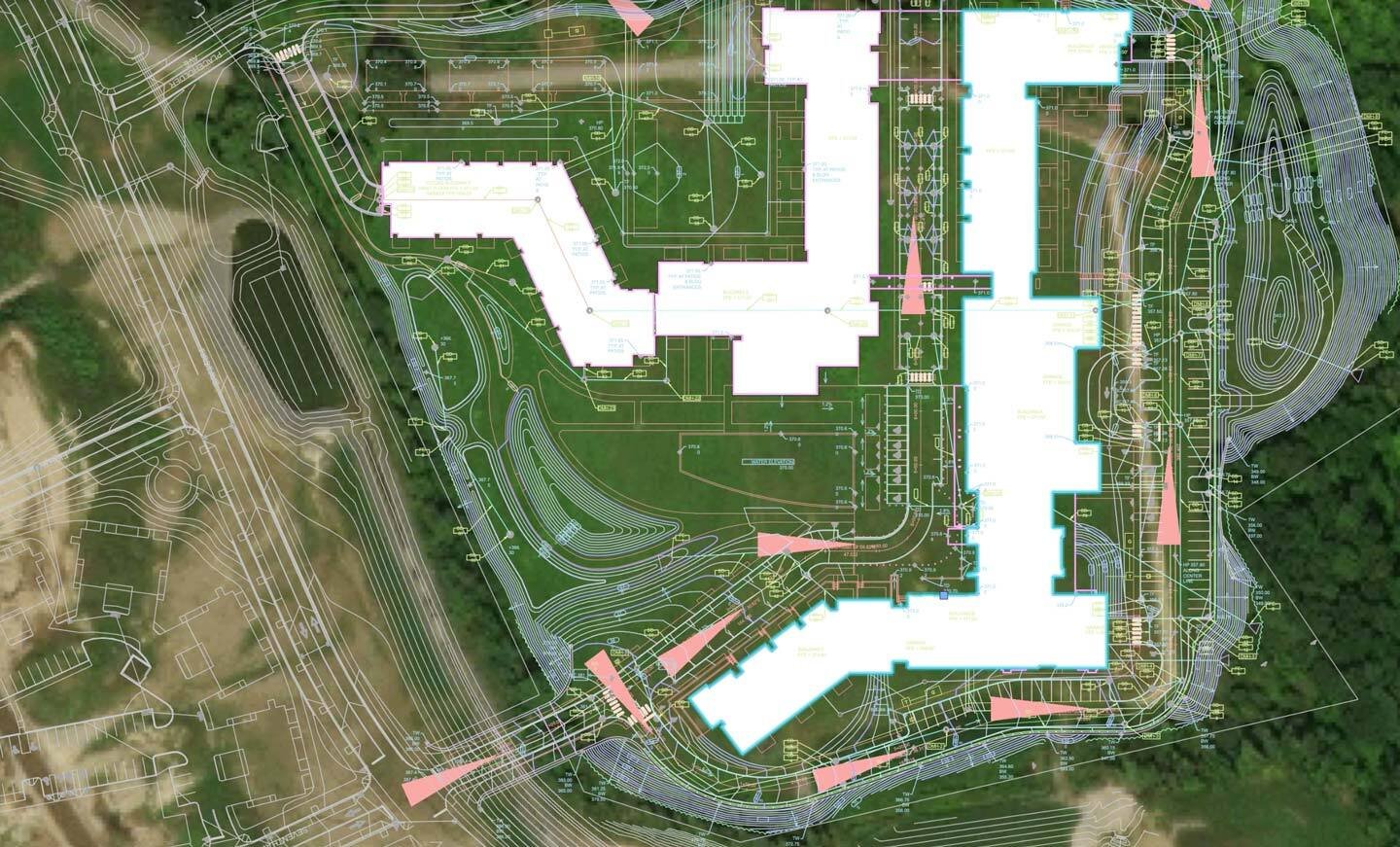
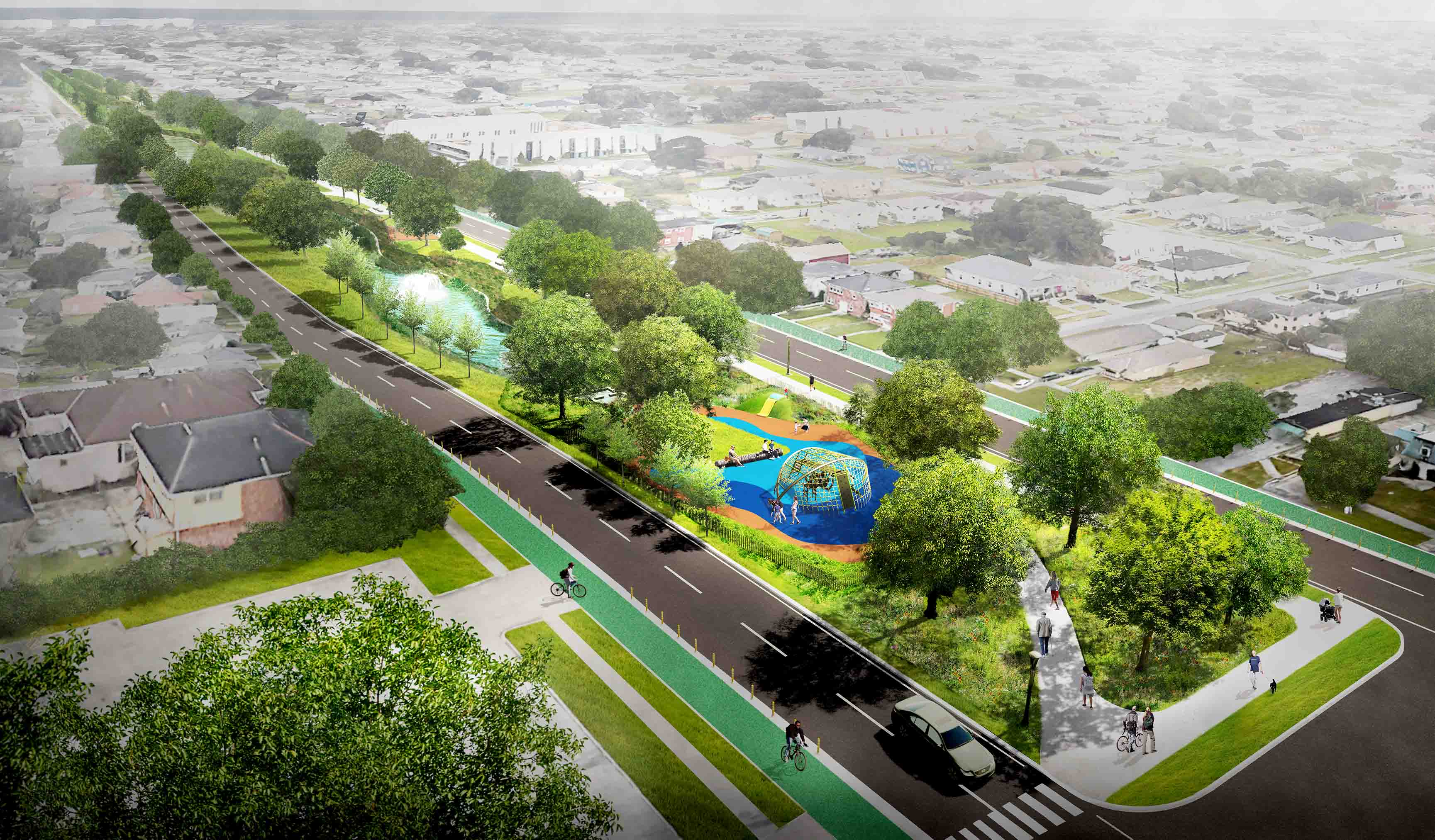
GIS-based analysis: exploration, analysis, and synthesis of landscape architectural compositions to expose latent architectural relationships, while employing computers’ processing capacity and capabilities for ex-ante and ex-post simulation and evaluation.
GIS-based modeling: data acquisition and the description of existing and future landscape design compositions in digital form
GIS-based visual representation: the representation of (virtual) landscape architectural compositions in space and time in order to collect and transmit landscape design information and knowledge.
These processes have a high potential for measuring relevant and new features of landscape architectural compositions, as well as providing new methods of comprehending them. Using the basic principles of study in landscape architecture as a starting point for computer-aided architectonic analysis, a ‘toolbox’ for GIS-based landscape design research emerges. This toolbox is a collection of GIS-analysis methods and approaches organized according to landscape architecture concepts. Hence, notions of GIS-based analysis can be integrated and applied in accordance with landscape architects’ experience.