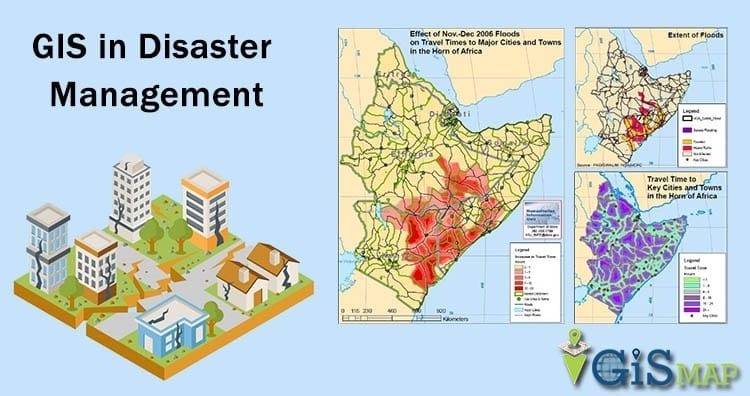
Disaster management is a multidisciplinary process aimed at reducing the impact of natural and human-induced hazards. It involves four phases: mitigation, preparedness, response, and recovery. A critical component of all these phases is mapping, which provides spatial information on risk areas, resources, infrastructure, and the extent of disaster impacts. By employing Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and cartographic tools, mapping serves as a vital decision-support system in both pre- and post-disaster scenarios.
Mapping Before Disaster (Pre-Disaster Mapping)
Pre-disaster mapping focuses on preparedness and mitigation. It helps in identifying hazard-prone areas and guiding policies to reduce vulnerabilities.
- Key Relevance of using Drone and GIS for Pre-Disaster Management:
- Hazard Zonation and Risk Identification: This is very necessary in disaster management as it helps in classifying hazard areas for necessary actions to be undertaken. This is highlighted as follows:
- Mapping floodplains, fault lines, coastal erosion zones, and industrial hazards helps identify populations and infrastructure at risk.
- Supports the design of hazard vulnerability maps (HVMs) and risk atlases.
- Early Warning Systems: In disaster management the early warning system involves:
- Integration of meteorological, hydrological, and seismic data with maps enhances real-time monitoring and forecasting.
- Example: flood forecast maps and storm surge prediction models.
III. Resource and Infrastructure Mapping: This very paramount in disaster management and it involves:
- Identifies critical facilities such as hospitals, schools, fire stations, and evacuation routes.
- Facilitates pre-positioning of relief materials and planning of emergency response logistics.
- Community Awareness and Preparedness: The public in the disaster zones are to be intimated on the issues at hand on disaster and preparation towards such is key.
- Maps are tools for educating communities about local hazards and evacuation routes.
- Helps policymakers in zoning laws, land-use planning, and enforcement of building codes.
Mapping After Disaster (Post-Disaster Mapping)
Post-disaster mapping is primarily for response and recovery. It assesses the extent of damage, guides relief operations, and supports reconstruction efforts.
- Key Relevance of using Drone and GIS for Post-Disaster Management:
- Damage Assessment and Impact Analysis: The major factors involved in these aspects are:
- Satellite imagery and aerial photography provide rapid information on destroyed buildings, flooded areas, burnt forests, and collapsed infrastructure.
- Enables quick estimates of casualties, displacement, and resource loss.
- Relief and Humanitarian Aid Distribution: After disaster occurrence mapping of affected victims is very important in order to help them. The essence of this include:
- Mapping helps identify affected populations and inaccessible areas, ensuring that aid is equitably distributed.
- Supports coordination among humanitarian agencies, government bodies, and NGOs.
III. Search and Rescue Operations: The application of GIS in searching and rescuing operations is essential in the following ways:
- GIS-based maps help rescue teams navigate debris, collapsed structures, and blocked roads.
- Real-time maps can update changes as rescue progresses.
- Monitoring Recovery and Rehabilitation: GIS is a powerful tool that can be used to create a map of where disaster occurred and show the extent of what has been done (or or on going) to restore the normalcy in the areas affected: the following underscore the relevance:
- Post-disaster mapping tracks the progress of reconstruction and rehabilitation.
- Ensures that rebuilding follows safer land-use patterns and resilient infrastructure planning.
- Policy Feedback and Future Mitigation: Map has the ability to show clearly the state of the environment during the pre and post disaster which is helpful in policy making. The facts below prove the essence of this:
- By comparing pre and post-disaster maps, stakeholders gain insights into weaknesses in planning and resilience strategies.
- These lessons guide future disaster mitigation and preparedness frameworks.
Integration of Pre- and Post-Disaster Mapping in Disaster Management
The synergy between pre and post-disaster mapping is vital as highlighted in the following context:
- Before disaster: maps highlight potential vulnerabilities.
- After disaster: maps confirm actual impacts, enabling calibration of hazard models and validation of risk predictions.
This integration strengthens the disaster risk reduction (DRR) cycle, making future responses more effective.
Effective disaster management is incomplete without the use of spatial mapping technologies as a central tool for safeguarding lives, infrastructure, and the environment. The flowchart diagrams (Figure 1.1 and Figure 1.2) show the role of mapping in pre- and post-disaster phases. It highlights how Pre-Disaster Mapping supports hazard zonation, forecasting, resource planning, and preparedness, while Post-Disaster Mapping supports damage assessment, relief, rescue, and recovery.
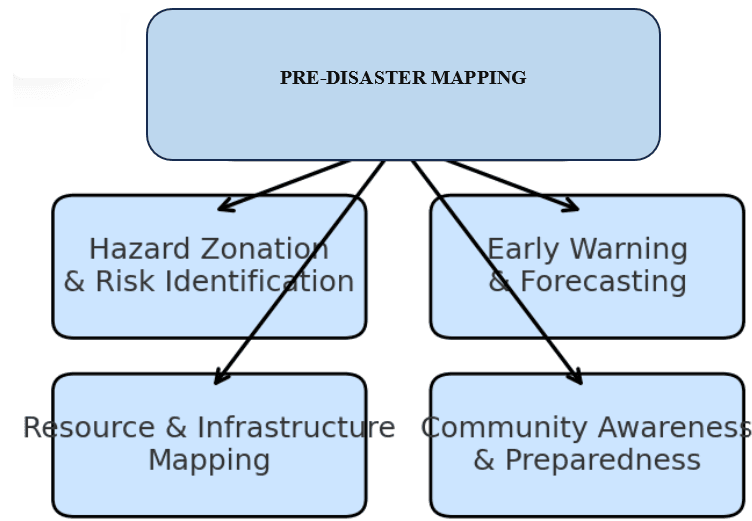
Figure 1.1: Pre-Disaster Mapping
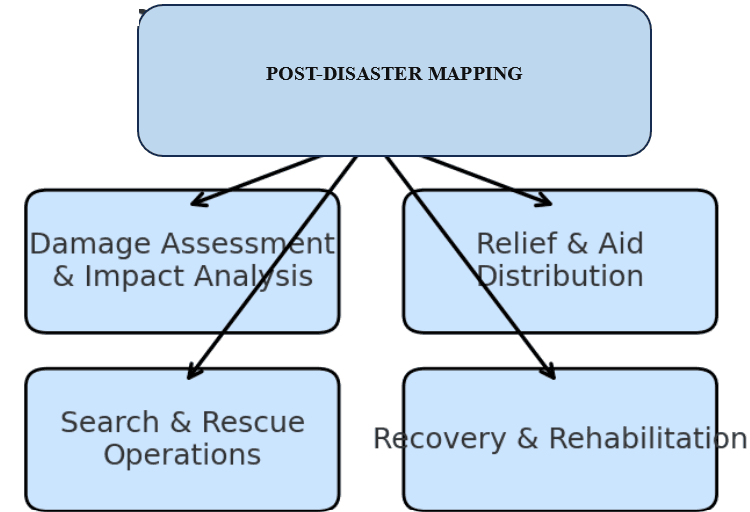
Figure 1.2: Post Disaster Mapping
Conclusion
Mapping before and after disasters is not merely a technical exercise; it is a lifeline of disaster management. Pre-disaster mapping enhances preparedness, mitigation, and resilience, while post-disaster mapping enables rapid response, recovery, and learning for the future. Together, they ensure that disaster management is proactive rather than reactive, evidence-based rather than speculative, and sustainable rather than temporary.
Geoinfotech Resources Ltd is a surveying and GIS company who can help in disaster management in Nigeria and any country in which this service is required. Contact us for the best and satisfactory services in disaster prevention and control for environmental sustainability including protection of lives and properties.