Geographical Information Systems (GIS) have evolved from simple mapping tools to increasingly being vital in various sectors globally, and Nigeria is no exception. The country has started leveraging GIS to tackle complex challenges in public health, logistics, and urban planning. This technology enables more informed decision-making, resource allocation, and efficient management of urban and rural spaces. Key applications of GIS are in disease tracking, logistics, and smart city planning in Nigeria
GIS in Disease Tracking
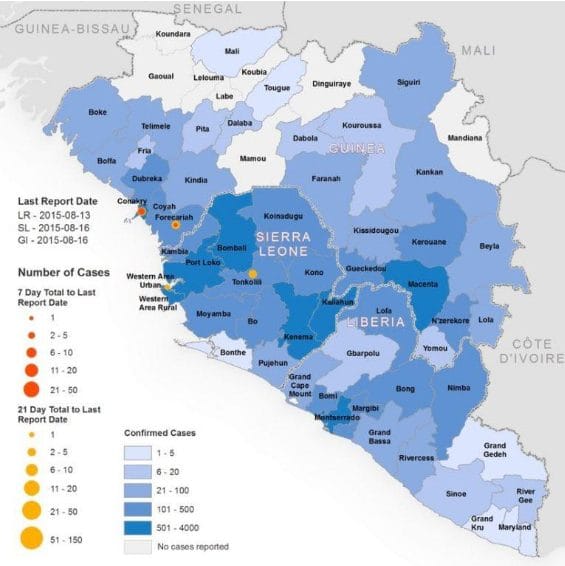
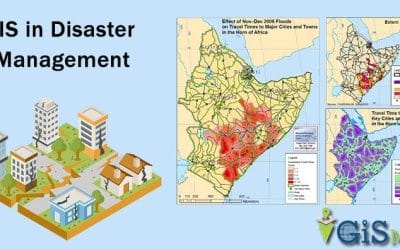
In Nigeria and Africa as a whole, GIS has played an essential role in tracking and controlling the spread of infectious diseases, which have historically posed a major health challenge. GIS helps health authorities track disease outbreaks, visualize spatial patterns, and allocate resources efficiently.
Applications:
- Disease Surveillance and Outbreak Response: GIS helps in real-time monitoring of disease outbreaks like cholera, Lassa fever, yellow fever, and more recently, COVID-19. Mapping outbreak zones enables targeted interventions.
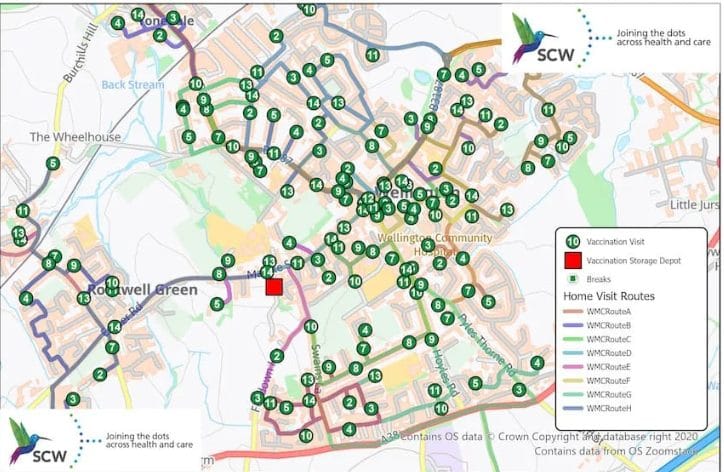
- Vaccination Campaigns: GIS is instrumental in planning and monitoring vaccination campaigns, ensuring vaccines reach rural and underserved areas.
- Public Health Planning: It assists in the strategic placement of healthcare facilities and medical resources, guiding government responses to health emergencies.
- Track infectious diseases: Monitor the spread of diseases like Ebola, COVID-19, and malaria to implement effective containment measures.
Real-World Example:
- Ebola Outbreak in West Africa (2014): While Nigeria was fortunate to experience fewer Ebola cases than some of its neighbors, GIS played a vital role in containing the outbreak. Authorities used GIS to map and track Ebola cases, identify potential areas of concern, and track individuals who may have been in contact with infected people. GIS was also used to plan isolation and treatment centers.
- COVID-19 Tracking and Response: During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) relied on GIS for real-time tracking of COVID-19 cases across the country. GIS maps displayed the spread of the virus and helped allocate resources like testing kits, PPE, and medical teams to hotspots, improving response time.
- Malaria Control in Rural Areas: GIS is used in malaria surveillance in Nigeria, particularly in the northern and southern parts of the country where malaria is endemic. GIS data helps public health agencies to map hotspots and target interventions like indoor spraying with insecticides and distribution of mosquito nets.
- The Nigeria Center for Disease Control (NCDC) utilizes GIS to track and map the spread of infectious diseases, including Lassa fever and yellow fever. This spatial analysis helps identify vulnerable communities and target preventive measures accordingly.
GIS in Logistics
The logistics sector is crucial to any nation’s economy, with supply chains moving goods between cities and rural areas. GIS is being utilized to streamline transportation, improve route planning, and reduce delays in delivery.
Applications:
- Route Optimization: GIS is employed by companies to optimize routes, reducing fuel consumption, travel time, and operational costs. It helps identify the best paths and bypass congested areas, especially in traffic-prone cities like Lagos.
- Warehouse and Distribution Network Planning: GIS helps businesses to locate warehouses close to key transportation hubs and markets, improving inventory management and delivery efficiency.
- Real-Time Monitoring of Goods: With GIS, logistics companies can track goods in transit, ensuring that customers receive accurate delivery times and that goods are transported securely.
Real-World Example:
- Lagos Port Logistics: Lagos, with its busy ports and heavy traffic congestion, has seen improvements in logistics efficiency through GIS-based route optimization. Companies like Dangote Group and Maersk use GIS to track shipments, optimize distribution routes, and reduce delivery times. By analyzing data from GIS systems, these companies can avoid traffic bottlenecks and more efficiently move goods through the busy port and urban areas.
- Jumia’s E-commerce Logistics: Nigeria’s leading e-commerce platform, Jumia, utilizes GIS to optimize its delivery routes across cities like Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt. By integrating GIS with real-time data, Jumia is able to ensure faster deliveries, which is critical to maintaining customer satisfaction in Nigeria’s competitive online retail market.
GIS in Smart City Planning
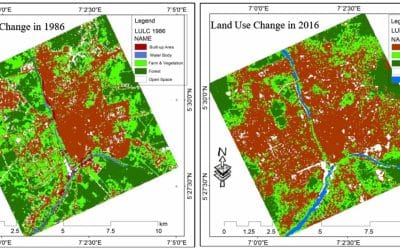
Nigeria’s cities, especially Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt, are facing rapid urbanization, leading to traffic congestion, poor waste management, and infrastructure challenges. GIS is being used in smart city planning to address these urbanization challenges and create more sustainable, efficient, and livable cities.
Applications:
- Urban Planning and Infrastructure Management: GIS supports the design and management of urban infrastructure, helping city planners map roads, utilities, green spaces, and housing developments.
- Traffic and Transportation Management: GIS is used to monitor traffic flows and plan transportation systems, aiming to reduce congestion and improve public transportation services.
- Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability: GIS aids in managing urban ecosystems, monitoring air and water quality, and planning for renewable energy sources like solar power.
Real-World Example:
- Lagos Smart City Initiatives: The Lagos State government has begun using GIS for planning smart city initiatives, particularly around traffic management. GIS is used in the Lagos Traffic Management Authority (LASTMA) to optimize traffic flow by analyzing real-time traffic data. Additionally, GIS is being used to design pedestrian walkways and cycling lanes to promote sustainability.
- Abuja Smart City Development: Abuja, the capital city of Nigeria, is exploring the integration of GIS in its urban development projects. The Nigerian government has begun developing a smart city in the heart of Abuja, where GIS will be used for land management, water supply networks, waste management, and energy optimization.
- Port Harcourt Urban Renewal: The Port Harcourt Urban Renewal Project involves the use of GIS for mapping the city’s infrastructure, including roads, sewage systems, and housing. The GIS platform is also used to optimize public services and environmental monitoring, ensuring the city’s growth is sustainable.
Conclusion
GIS offers the potential for smarter, more efficient solutions. With continued investment in GIS technology and data analytics, Countries can improve its public health systems, streamline logistics operations, and build cities that are both livable and sustainable.
In Nigeria, GIS is transforming the way disease tracking, logistics, and urban planning are approached. Its applications are crucial for improving public health outcomes, optimizing supply chain management, and building smarter, more sustainable cities. Real-world examples like the use of GIS in COVID-19 tracking by the NCDC, logistics optimization in Lagos, and smart city planning in Abuja and Lagos demonstrate how GIS is helping Nigeria tackle its most pressing challenges.