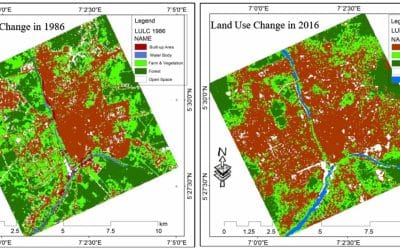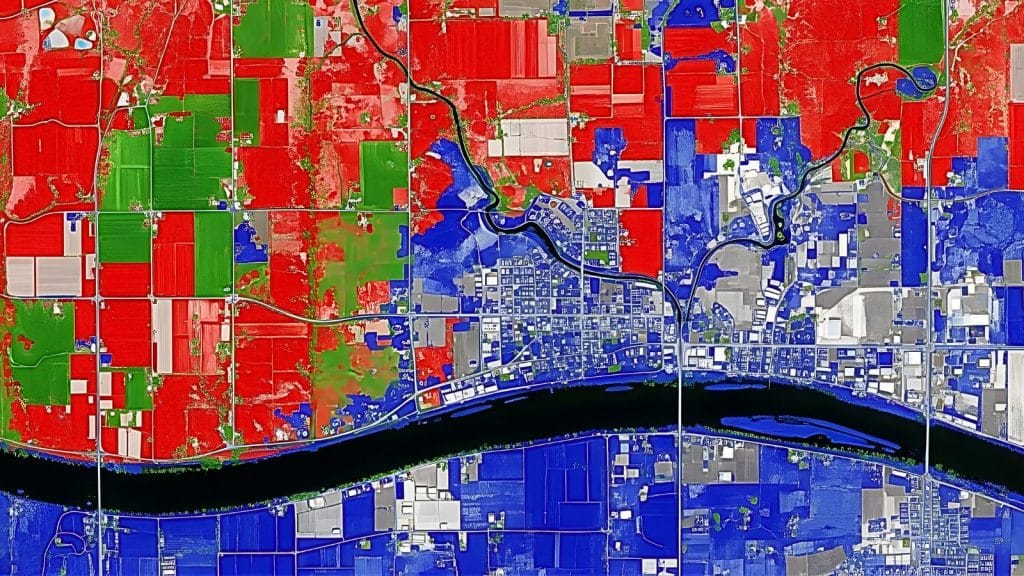
Photogrammetry is changing the way we collect, analyze, and visualize spatial data. The application of photogrammetry allows surveyors, engineers, and GIS professionals to create accurate 3D models from photographs captured by drones or cameras. Moreover, this technology has become essential for mapping, land development, construction, and environmental management across Nigeria and beyond.
What Is Photogrammetry?
Photogrammetry is the science of obtaining reliable measurements and models from photographs. In practice, it combines overlapping images to create 3D representations of objects or terrain. In addition, the application of photogrammetry provides a fast, affordable, and highly precise alternative to traditional ground surveying.
Today, drones and satellites make photogrammetry more accessible. Professionals now use UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) to capture high-resolution images from above, while software such as Pix4D, Agisoft Metashape, and DroneDeploy processes the imagery into accurate maps and 3D surfaces.
Applications of Photogrammetry in Mapping and Surveying
The application of photogrammetry is extensive in modern mapping and geospatial workflows.
Land and Urban Planning
Photogrammetry helps planners visualize and analyze land-use patterns. For instance, high-resolution orthophotos assist local governments in monitoring urban growth and infrastructure development.
Construction and Engineering
Surveyors use drone photogrammetry to generate digital elevation models (DEMs) and contour maps. Consequently, construction teams can measure volumes, monitor progress, and ensure design accuracy with minimal time and cost.
Agriculture and Forestry
In agriculture, aerial photogrammetry supports crop health analysis and land optimization. Moreover, foresters use it to estimate biomass, monitor deforestation, and plan sustainable resource management.
Environmental Monitoring and Disaster Management
Photogrammetry helps identify flood zones, erosion areas, and environmental degradation. As a result, emergency managers can respond faster and allocate resources efficiently.
Use of Drones in Modern Photogrammetry
Drones have revolutionized the application of photogrammetry by simplifying aerial data collection. They fly programmed routes, capturing overlapping images that photogrammetric software later stitches into 3D models.
In addition, drones enable surveyors to reach inaccessible terrain and collect data in real time. Their precision, combined with GNSS and RTK positioning, ensures centimeter-level accuracy for professional projects.
Geoinfotech’s drone mapping services in Nigeria utilize advanced photogrammetry to produce accurate 3D maps for land surveyors and construction firms.
Advantages and Limitations of Photogrammetry
Advantages:
- Provides high-resolution and accurate 3D data.
- Reduces survey time and field costs.
- Integrates easily with GIS, CAD, and BIM platforms.
- Supports large-area mapping with minimal equipment.
Limitations:
- Accuracy depends on image overlap, lighting, and camera quality.
- Processing large datasets can be time-consuming.
- Requires trained professionals for flight planning and data processing.
However, when combined with modern drones and processing software, these challenges are easily managed, making photogrammetry a standard tool for modern surveyors.
Future of Photogrammetry in Nigeria’s Geospatial Industry
The future of photogrammetry in Nigeria looks promising. As technology advances, drone regulations and GNSS accuracy improvements will support more reliable and scalable data capture. Furthermore, institutions like Geoinfotech are providing hands-on training for professionals who want to master drone photogrammetry and 3D mapping techniques.
Ultimately, the application of photogrammetry will continue to enhance decision-making, improve project delivery, and strengthen the nation’s geospatial infrastructure.
Conclusion
Photogrammetry has become a game-changer for surveying, construction, and environmental management. Through the application of photogrammetry, professionals can capture, analyze, and visualize the world with unmatched accuracy. Therefore, mastering this technology is essential for anyone working in mapping, geoinformatics, or spatial data science.