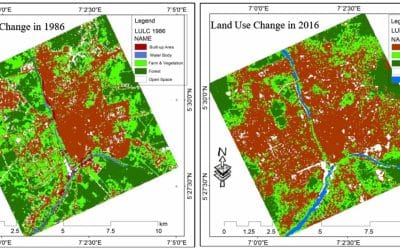
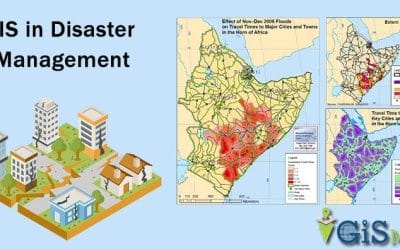
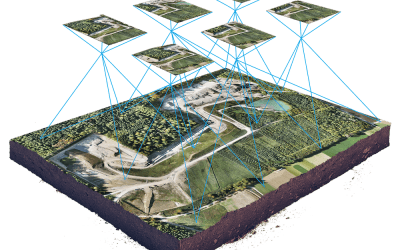
To automate GIS workflows in ArcGIS Pro using Python and ArcPy, you can write Python scripts that leverage the ArcPy module to access and manipulate geospatial data within your project, utilizing various geoprocessing tools to perform tasks like data selection, analysis, transformation, and visualization, all within the ArcGIS Pro environment; essentially, you’re writing code to execute a series of GIS operations programmatically instead of doing them manually through the interface.
Key Steps:
Import ArcPy: Start your Python script by importing the ArcPy module, which provides access to all the necessary functions and classes for interacting with ArcGIS Pro.

Set Workspace: Define the active workspace where your data resides using the arcpy.env.workspace property. Code: arcpy.env.workspace

Access Data: Use ArcPy functions to access and manipulate data like feature classes, tables, and raster datasets.

Execute Geoprocessing Tools: Call geoprocessing tools provided by ArcPy to perform GIS operations like buffering, selecting features, calculating fields, or performing spatial analysis.

Iterate through Data: Use loops to process multiple features or datasets within your workflow.

How to Use Python in ArcGIS Pro:
Python Window: Open the Python window within ArcGIS Pro to execute short snippets of code interactively.

Script Tool: Create a custom geoprocessing tool within your project by writing a Python script and defining input/output parameters.
ArcGIS Notebooks: Utilize the Jupyter Notebook-like environment in ArcGIS Pro to combine code, visualizations, and text for a more comprehensive analysis workflow.
Example Workflow:
- Task: Buffer all parcels within a specific zoning district by 100 meters and then select parcels that intersect with a proposed development area.

Key Considerations:
Understanding ArcPy Syntax: Familiarize yourself with ArcPy functions and their parameters to effectively manipulate geospatial data.
Error Handling: Implement error handling mechanisms to gracefully manage potential issues during script execution.
Optimization: Consider techniques to improve script performance, such as using spatial indexes and efficient data access methods.