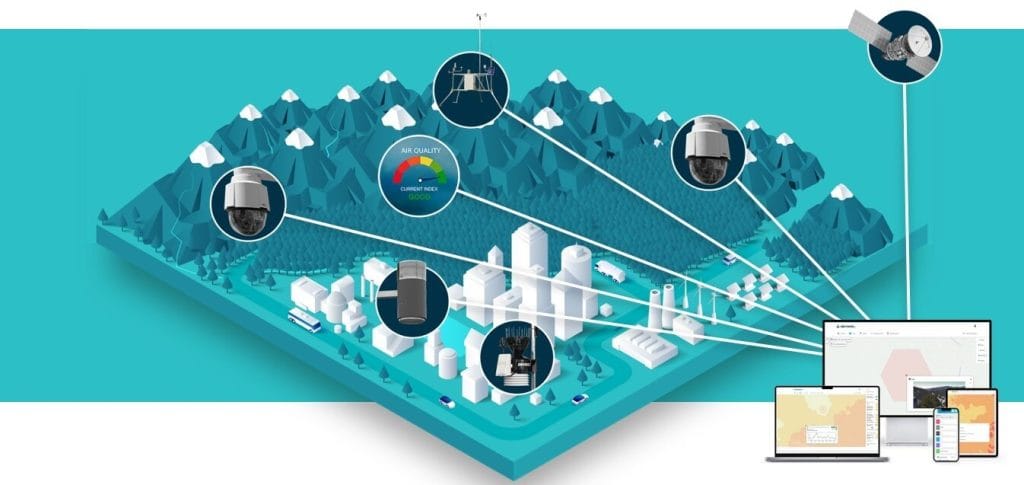
Field-based data collection has always been a crucial component of environmental studies, urban planning, agriculture, health monitoring, disaster management, and infrastructure development in Nigeria. However, the true value of such information lies in its ability to be integrated, shared, and analysed in real time across platforms. Recent advancements in web GIS Nigeria technologies now allow seamless field data integration Nigeria, enabling organisations to move beyond traditional static maps and towards dynamic GIS web apps Nigeria and real-time GIS dashboards Nigeria. This article provides a scientific and practical exploration of how field data is being brought to the web in Nigeria, the enabling technologies, benefits, applications, challenges, and recommendations for sustainable adoption.
Concept of Field Data Integration
Field data integration involves combining data collected from field surveys (using GPS devices, mobile apps, UAVs, IoT sensors, etc.) with centralised GIS platforms for storage, processing, and visualisation. In Nigeria, this process has become essential in sectors such as land administration, environmental management, agriculture, and disaster risk reduction.
Field Data Integration Nigeria
- Agricultural extension workers in Kaduna and Kano states rely on field data integration in Nigeria methods to upload crop yield data into central servers.
- Hydrological studies in the Niger Delta use mobile sensors for real-time water quality monitoring and transmit this information via web GIS Nigeria systems.
GIS Web Apps
GIS web apps are web-based platforms that allow users to interact with spatial data, visualize patterns, and make informed decisions.
- GIS web apps in Nigeria are increasingly applied in land titling systems (e.g., Abuja Geographic Information Systems – AGIS), where landowners can check land status online.
Online Mapping
Online mapping enables dynamic visualisation of field-collected data through interactive maps accessible via the internet.
- Online mapping in Nigeria has transformed how citizens and decision-makers access geographic information. For instance, flood-prone areas in Anambra and Bayelsa are mapped in real time to guide evacuation efforts.
Concept of Real-time GIS Dashboards
A real-time GIS dashboard is an interactive interface that provides live updates from field data streams. These dashboards integrate spatial, temporal, and statistical data for rapid interpretation.
Real-time GIS Dashboard Nigeria
- The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) uses real-time GIS dashboard Nigeria to track disease outbreaks, integrating case reports from the field with national health databases.
- During flooding in Kogi State, real-time dashboards display rising water levels and affected communities, assisting in emergency response.
Web GIS Nigeria
Web GIS Nigeria represents the backbone of bringing field data to the web, combining server technologies, cloud computing, and web services for nationwide accessibility. It supports:
- Multi-user access across ministries, universities, and private sectors.
- Integration of raster (satellite) and vector (survey) data into a single accessible environment.
- Cross-platform compatibility (mobile, tablet, desktop).
Benefits of Bringing Field Data to the Web in Nigeria
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Timely access to real-time GIS dashboards for flood monitoring and disaster risk management.
- Transparency: Public access to online mapping Nigeria for land records reduces disputes and corruption.
- Collaboration: Multi-stakeholder projects use GIS web apps Nigeria to unify datasets from field surveys and satellite imagery.
- Efficiency: Reduced duplication of field surveys through shared web GIS Nigeria platforms.
- Scalability: Cloud-hosted systems can handle expanding datasets from UAVs, IoT, and crowd-sourced citizen science.
Applications of Bringing Field Data to the Web in Nigeria
- Land Administration: AGIS and state-level GIS platforms use online mapping in Nigeria to streamline land titling.
- Agriculture: Field data integration Nigeria allows monitoring of farmlands for precision agriculture.
- Public Health: COVID-19 cases were tracked using real-time GIS dashboard Nigeria solutions.
- Disaster Management: Flood and erosion monitoring in the Niger Delta relies on web GIS Nigeria systems.
- Transportation: GIS web apps Nigeria help monitor and visualise traffic congestion in Lagos.
Challenges of Bringing Field Data to the Web in Nigeria
- Infrastructure Deficit: Limited broadband internet access in rural areas,
- Data Gaps: Lack of standardised methods for field data integration Nigeria,
- Capacity Limitations: Insufficient skilled GIS professionals,
- Funding Constraints: High cost of cloud hosting and server maintenance, and
- Policy Barriers: Weak geospatial data-sharing frameworks.
Conclusion
Bringing field data to the web in Nigeria represents a transformative step toward effective governance, sustainable resource management, and rapid disaster response. Through field data integration, GIS web apps, online mapping, and real-time GIS dashboards, Nigeria is moving toward a data-driven society. The adoption of web GIS Nigeria provides a foundation for transparent, collaborative, and efficient spatial data management—helping the country achieve its development goals in the era of digital transformation.