To manage and create geodatabases in ArcGIS Pro, you primarily use the Catalog pane, where you can right-click on a desired folder to create a new file geodatabase, and then further manage its contents by adding feature classes, tables, and other datasets directly within the geodatabase; for enterprise geodatabases, you utilize geoprocessing tools to connect to a database server and create the geodatabase within that environment.
Key steps for creating a File Geodatabase in ArcGIS Pro:
- Open ArcGIS Pro: Launch the software and open your project.
- Access the Catalog pane: Go to “View” on the interface, then click on the “Catalog pane”
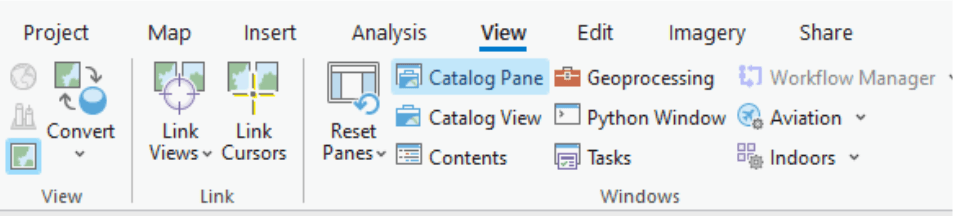
- Ensure the Catalog pane is visible on the left side of the interface.
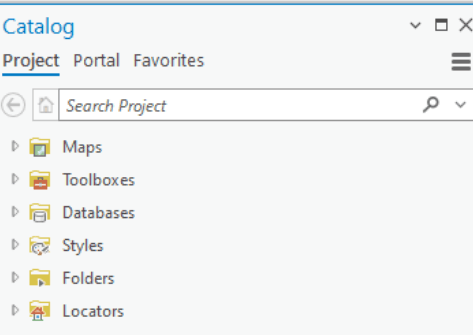
- Navigate to the desired location: In the Catalog pane, browse to the folder where you want to create the geodatabase.
- Right-click and select “New”: Right-click within the folder and choose “New” > “File Geodatabase”.
- Name the geodatabase: Enter a name for your new geodatabase.
Managing data within a geodatabase:
- Add new datasets: Right-click on the geodatabase in the Catalog pane, select “New” and then choose the type of dataset you want to create (like feature class, table, or feature dataset).
- Edit feature class properties: Double-click on a feature class to open its properties dialog where you can modify attributes, geometry type, spatial reference, and other parameters.
- Delete datasets: Right-click on a dataset within the geodatabase and select “Delete” to remove it.
Creating an Enterprise Geodatabase:
- Access the geoprocessing tool: Open the “Create Enterprise Geodatabase” tool from the Data Management toolbox.
- Specify database connection details: Provide information like the database server, database name, username, and password.
- Set geodatabase properties: Define the schema where the geodatabase will be created and set a password for the geodatabase administrator.
- Run the tool: Click “Run” to create the enterprise geodatabase.
Important considerations:
- Geodatabase types: ArcGIS Pro supports various geodatabase types including file geodatabases, personal geodatabases, and enterprise geodatabases, each with its own storage and access capabilities.
- Data management tools: Utilize geoprocessing tools to perform advanced data management tasks like editing attributes, creating topologies, and managing relationships between datasets.
- Permissions and access control: When working with enterprise geodatabases, ensure appropriate user permissions are set to manage data access and editing rights.