Smart cities are rapidly emerging as a transformative model for urban development, particularly across Africa where urbanization is accelerating. As governments and city planners grapple with challenges like overcrowding, waste management, traffic congestion, and housing shortages, geospatial technology is proving to be a powerful ally. This blog post explores the critical role of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial data analytics in enabling smarter, more efficient African cities.
What is a Smart City?
A smart city leverages digital technology and data-driven insights to improve the quality of life for its citizens. It integrates information and communication technology (ICT) with physical infrastructure and services to optimize operations and enhance sustainability. Geospatial technology is central to this integration, providing the spatial intelligence necessary for informed decision-making.
Geospatial Technology:
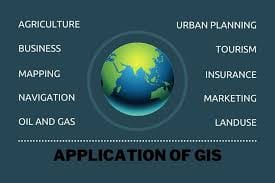
The Foundation of Smart Cities Geospatial technologies such as GIS, remote sensing, GPS, and spatial data analytics are fundamental to smart city development. These tools allow city managers to visualize, analyze, and interpret data to better understand spatial patterns and relationships. Here are some practical applications:
- Urban Planning and Land Use: GIS enables cities to design zoning plans, monitor land use, and detect unauthorized developments.
- Traffic and Transportation: Real-time GPS data helps optimize traffic flow, plan public transport routes, and manage logistics.
- Waste Management: Spatial data can track waste collection routes and identify areas with service gaps.
- Disaster Management: Remote sensing and GIS help in risk mapping, early warning systems, and emergency response planning.
African Success Stories
- Kigali, Rwanda: Kigali has become a model for smart urban planning in Africa. With a centralized GIS platform, the city manages land registration, infrastructure planning, and service delivery more efficiently.
- Lagos, Nigeria: Lagos State has implemented a GIS-based land information system that streamlines property registration and taxation, improving government revenue and transparency.
- Cape Town, South Africa: The city uses spatial analytics to address crime hotspots, optimize public services, and manage utilities like water and electricity more effectively.
Challenges to Overcome
Despite the promising developments, several challenges hinder the full adoption of geospatial technologies in African cities: – Limited Access to Quality Data: Many cities lack up-to-date spatial data. – Funding Constraints: Infrastructure and software investments can be expensive. – Skilled Workforce Shortage: There is a need for more trained geospatial professionals. – Policy and Governance Issues: Institutional support and policy frameworks are often inadequate.
Opportunities Ahead
The future is bright for geospatial innovation in Africa. Emerging trends include: – Integration with AI and IoT: Combining GIS with Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things enhances predictive analytics for smarter urban management. – Open Data Platforms: These can encourage transparency and citizen engagement. – Capacity Building: Training programs and academic courses are expanding across the continent to build local expertise.
Conclusion
Geospatial technology is not just supporting Africa’s smart city revolution—it is driving it. From improving basic infrastructure to fostering inclusive growth, spatial tools empower cities to be more responsive, sustainable, and livable. By investing in geospatial infrastructure and education, African nations can build cities that truly work for everyone.
Call to Action Are you a student, urban planner, or tech enthusiast? Start learning geospatial tools like QGIS, ArcGIS, and remote sensing software. Join local initiatives and hackathons focused on smart cities. The future of Africa’s urban spaces is spatial—and you can be part of building it.