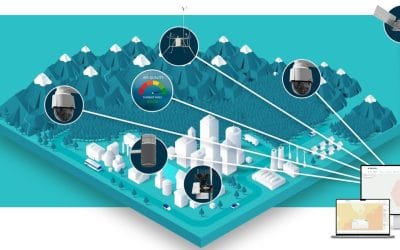
In an era defined by data, the fusion of Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing how we understand and interact with the world around us. This powerful triad is enabling smarter decisions in urban planning, agriculture, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and more ushering in a new age of spatial intelligence.

Understanding the Technologies
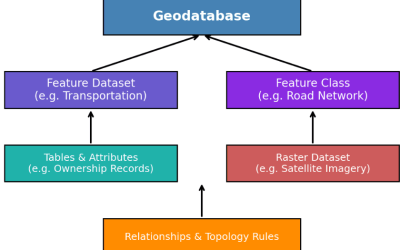
GIS is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and present spatial or geographic data. It allows users to understand patterns, relationships, and geographic context through maps and analytics.
Remote Sensing involves the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact—typically through satellite or aerial sensors. It provides large-scale, real-time data on Earth’s surface and atmosphere. Artificial Intelligence, particularly machine learning and deep learning, refers to systems that can learn from data and make intelligent decisions. When integrated with spatial technologies, AI brings automation, accuracy, and predictive capabilities to geospatial analysis.

How AI Enhances GIS and Remote Sensing
- Automated Image Classification
AI algorithms, especially convolutional neural networks (CNNs), are being used to classify land cover, detect changes, and identify objects (e.g., buildings, roads, water bodies) from satellite images with high accuracy. This process, once manual and time-intensive, is now faster and more consistent.
- Predictive Modeling
AI models can forecast environmental phenomena like floods, wildfires, or crop yields by analyzing historical geospatial data combined with climate models and sensor inputs. These predictions are crucial for proactive decision-making in agriculture, disaster preparedness, and public health.
- Anomaly Detection
AI helps detect anomalies in satellite data—such as illegal deforestation, urban sprawl, or environmental degradation. This enables rapid response and better monitoring of protected areas.
- Data Fusion
AI facilitates the integration of data from multiple sources—e.g., combining drone imagery, satellite data, and ground sensors—to create a richer, multidimensional understanding of spatial phenomena.
- Real-Time Analytics
With AI, GIS platforms can process and analyze streaming data (like traffic flows, air quality, or social media geotags) in real-time, powering smart city applications and dynamic mapping systems.
Applications Across Industries
- Urban Planning: Planners use AI-enhanced GIS to model growth scenarios, optimize infrastructure placement, and manage resources efficiently.
- Agriculture: Precision agriculture uses AI and remote sensing to monitor crop health, detect pests, and optimize irrigation and fertilizer use.
- Disaster Management: AI predicts disaster-prone zones, assists in real-time damage assessment, and optimizes relief distribution using GIS layers.
- Environmental Conservation: AI aids in tracking biodiversity, mapping endangered habitats, and measuring the impact of climate change.
- Public Health: GIS and AI together track disease outbreaks, model spread patterns,and allocate healthcare resources effectively.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Despite its promise, the integration of AI with GIS and remote sensing comes with challenges:
- Data Quality & Availability:AI models require large, clean, and labeled datasets, which are not always accessible.
- Computational Resources: High-resolution imagery and real-time data processing demand significant computational power.
- Interpretability: Many AI models are “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand or justify decisions without explainable AI techniques.
Nonetheless, ongoing advances in cloud computing, open data initiatives, and AI research are steadily overcoming these barriers.
Lastly the integration of GIS, remote sensing, and AI is more than a technological trend—it is a paradigm shift. By combining the spatial awareness of GIS, the observational power of remote sensing, and the intelligence of AI, we are building a smarter, more responsive, and more sustainable world. As these technologies continue to evolve, their synergy will drive innovation in everything from climate resilience to urban ecosystems, making spatial intelligence a cornerstone of 21st-century progress.