What is Geoprocessing?
Geoprocessing is a framework and set of tools for processing geographic and related data. The comprehensive suite of geoprocessing tools can be used to perform spatial analysis or manage GIS data in an automated way
What Are Geoprocessing Tools?
Geoprocessing tools in ArcGIS Pro are functions that allow you to manipulate geographic data to derive new information. They include operations for analyzing spatial relationships, converting data formats, overlaying datasets, and much more. These tools are organized within the Geoprocessing pane, offering a user-friendly interface to execute complex workflows.
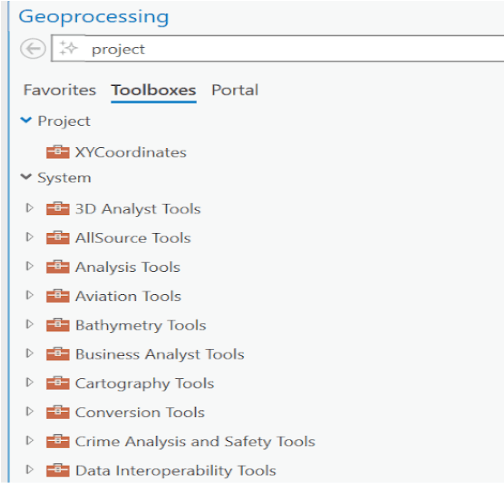
Key Benefits of Using Geoprocessing Tools
- Spatial analysis: Geoprocessing tools can help you compare places, find patterns, and make predictions.
- Better decision-making: Geoprocessing tools can help you find the best locations and paths and evaluate economic advantages.
- Improved efficiency: Geoprocessing tools can help you automate tasks and improve the efficiency of your work. Helps to automate repetitive tasks using models or scripts.
- Better communication: Geoprocessing tools can help you understand patterns and relationships, which can improve communication.
- Flexibility: Handle various data formats and types, including raster and vector data.
- Integration: Seamlessly combine tools into workflows to solve complex spatial problems.
Commonly Used Geoprocessing Tools in ArcGIS Pro
Here are some of the most frequently used tools and their applications:
- Buffer
- Purpose: Creates a zone around a feature at a specified distance.
- Application: Identifying areas impacted by a proposed infrastructure project.
- Clip
- Purpose: Extracts features of one layer based on the boundaries of another layer.
- Application: Isolating study areas from a larger dataset.
- Intersect
- Purpose: Identifies overlapping areas between two or more datasets.
- Application: Finding common ground between ecological zones and proposed mining areas.
- Dissolve
- Purpose: Aggregates features based on a specified attribute.
- Application: Merging administrative boundaries for regional analysis.
- Spatial Join
- Purpose: Transfers attributes from one layer to another based on spatial relationships.
- Application: Linking demographic data to geographic regions.
- Model Builder: A visual scripting language that allows you to build new tools that model your geoprocessing workflow
Steps to Use Geoprocessing Tools
- Open the Geoprocessing Pane: Navigate to the “Analysis” tab and click on “Tools” to open the Geoprocessing pane.
- Select a Tool: Browse or search for the desired tool in the Geoprocessing pane.
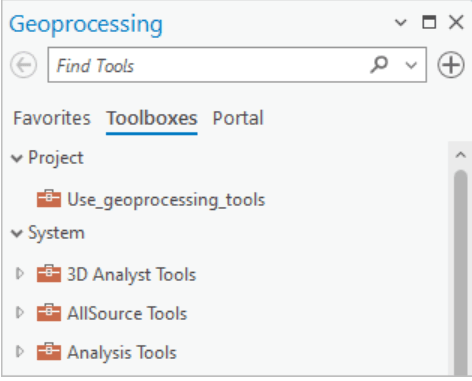
- Set Parameters: Define the input data, parameters, and output location.
- Run the Tool: Click “Run” to execute the operation. Monitor progress and check the output in the map view or attribute table.
- Save Results; Export the results to maintain a record of your analysis.
Automating Workflows with Model Builder and Python
ArcGIS Pro allows you to automate geoprocessing workflows using:
- Model Builder: A drag-and-drop interface to create visual workflows by chaining multiple tools.
- Python: Use the ArcPy library to script complex analyses and integrate geoprocessing with other data processing tasks.
Source: https://pro.arcgis.com/en/pro-app/latest/help/analysis/geoprocessing/modelbuilder/what-is-modelbuilder-.htm
Best Practices for Effective Geoprocessing
- Understand Your Data: Know the coordinate system, scale, and attributes of your datasets.
- Optimize Parameters: Test different settings to achieve the desired results.
- Document Workflows: Record steps to ensure reproducibility and shareability.
- Leverage Documentation: Utilize ArcGIS Pro’s extensive online help and tutorials for guidance.