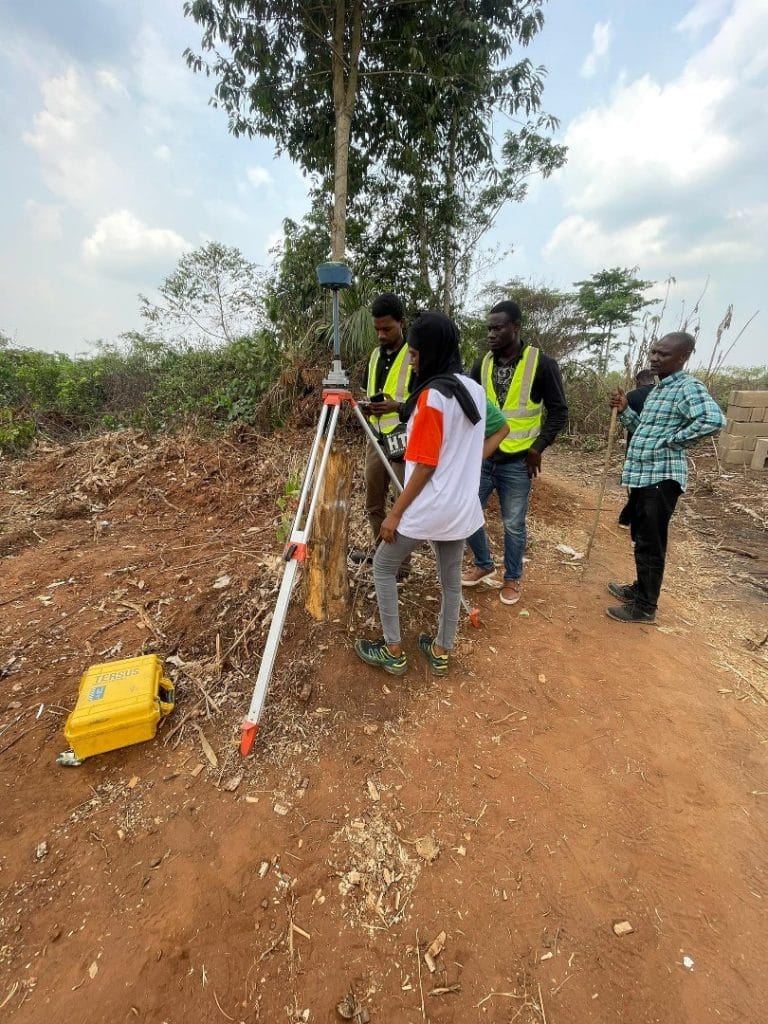
Accurate land records are the foundation of effective governance, property rights, and sustainable development. Yet in Nigeria, traditional cadastral surveying methods are often slow, expensive, and prone to disputes. With the rise of drone technology, the landscape of cadastral surveying in Nigeria is rapidly changing. By leveraging drones for land surveying, aerial photography, and drone mapping applications, surveyors can produce highly accurate maps in record time. This shift not only improves efficiency but also strengthens land administration and reduces conflicts over boundaries.
Accurate land records are the foundation of effective governance, property rights, and sustainable development. Yet in Nigeria, traditional cadastral surveying methods are often slow, expensive, and prone to disputes. With the rise of drone technology, the landscape of cadastral surveying in Nigeria is rapidly changing. By leveraging drones for land surveying, aerial photography, and drone mapping applications, surveyors can produce highly accurate maps in record time. This shift not only improves efficiency but also strengthens land administration and reduces conflicts over boundaries.
What is Drone-Based Cadastral Surveying?
Cadastral surveying refers to the mapping of land parcels for ownership, taxation, and development purposes. Traditionally, surveyors used ground-based tools such as total stations and GNSS receivers. While accurate, these methods are labour-intensive and time-consuming. Drone-based cadastral surveying, on the other hand, uses drone mapping software and drone surveying software to capture aerial images that are processed into high-resolution orthomosaic maps and 3D models. These products provide precise details of land boundaries, terrain, and infrastructure at a fraction of the cost and time of conventional methods.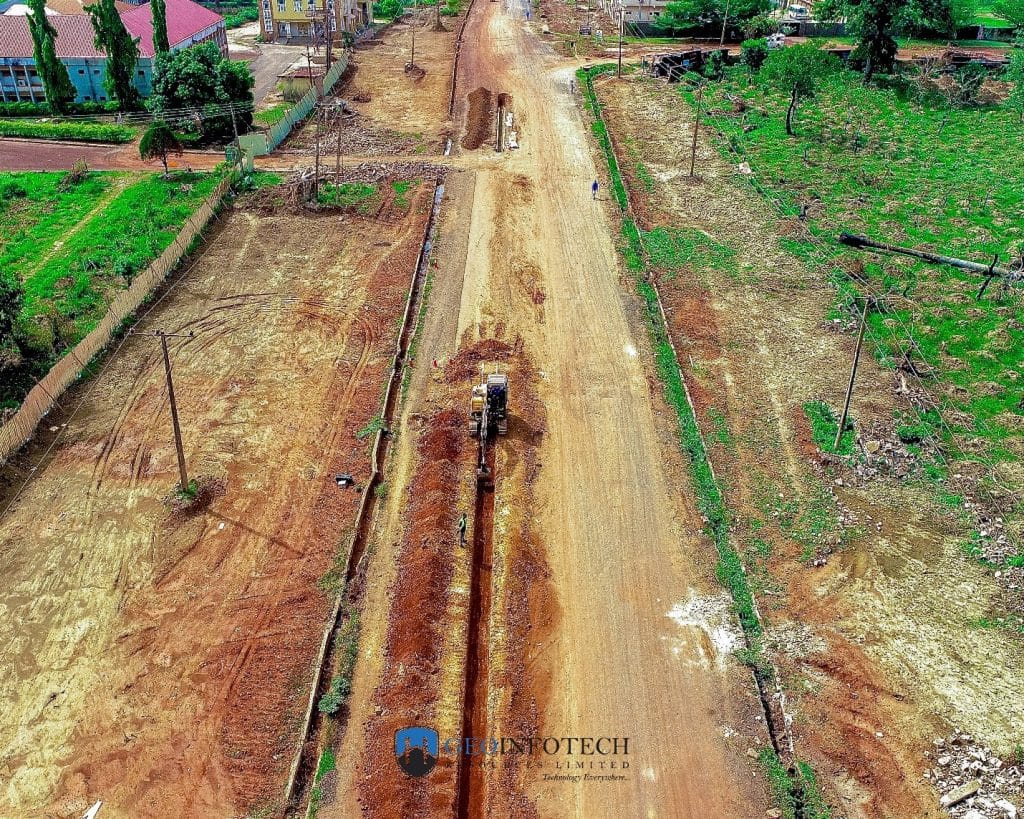
Key Benefits of Drone-Based Cadastral Surveying
1. High Accuracy and Precision
With advanced sensors and GNSS-enabled flight systems, drones for land surveying deliver centimetre-level accuracy. When combined with ground control points, drone data meets global cadastral standards for land registration.
2. Faster Data Collection
A process that once took weeks can now be completed in hours. For example, a drone can map hundreds of hectares in a single flight, producing detailed imagery ready for processing. This efficiency is particularly valuable in Nigeria, where demand for land documentation continues to grow.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Drone survey services in Nigeria significantly reduce manpower, equipment, and field time costs. Communities and government agencies can now access affordable land survey solutions that were once financially out of reach.
4. Enhanced Aerial Photography
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras capture detailed imagery of land parcels, buildings, and terrain. These images are invaluable for boundary verification, dispute resolution, and development planning.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Whether it is a small plot of land in a rural village or an expansive estate in Lagos, drone mapping applications can be tailored to any scale. This flexibility makes drones ideal for Nigeria’s diverse land management challenges.
Applications of Drone-Based Surveying in Nigeria
Land Registration and Documentation Unclear land ownership is a leading cause of disputes in Nigeria. Cadastral surveying with drones for mapping and surveying creates verifiable records that strengthen property rights and reduce conflicts. Urban Development and Planning Rapid urban growth requires precise land information. Drones provide up-to-date spatial data that urban planners use to design housing, roads, and infrastructure in expanding cities. Agriculture and Rural Land Management Farmers and cooperatives use drone technology to map farmland, monitor crop health, and optimize land use. Accurate maps also support government programs on agricultural land allocation. Infrastructure Projects From highways to pipelines, drones for land surveying ensure accurate route planning and land acquisition, minimizing disputes and delays.
Case Study: Drone Surveying in Nigerian Land Reforms
In states like Kaduna and Ogun, pilot projects have demonstrated the potential of drone survey services in Nigeria. By using drones to map rural communities, governments created accurate digital records of farmland, which were then used for issuing certificates of occupancy. This strengthened land tenure security, encouraged investment, and improved tax collection.
Challenges in Adopting Drone Surveying
- Regulatory Frameworks – Nigeria’s drone regulations are still evolving, and licensing can be a barrier for small survey firms.
- High Initial Costs – Though cheaper in the long run, drones and processing software require significant upfront investment.
- Skill Requirements – Professionals must be trained to operate drones and analyze resulting datasets.
- Community Acceptance – Some landowners may resist new technologies due to lack of awareness or mistrust.
The Future of Drone-Based Cadastral Surveying in Nigeria
As drone mapping software becomes more advanced and affordable, adoption in Nigeria is expected to accelerate. Integration with geospatial analysis and GIS technology will allow seamless land administration systems. Future possibilities include:
- Real-time cadastral updates through cloud platforms.
- Integration with blockchain for tamper-proof land records.
- 3D land parcel modelling for urban and rural development.
These innovations promise to transform how land is managed, making Nigeria’s land governance more transparent, efficient, and secure.
Conclusion
The benefits of drone-based cadastral surveying for land management in Nigeria are undeniable. From accuracy and speed to cost savings and scalability, drone survey services in Nigeria are reshaping how land is mapped and documented. By embracing drones for land surveying, government agencies, private firms, and communities can reduce disputes, boost investment, and support sustainable development. At the heart of this transformation is the combination of drone technology with cadastral surveying in Nigeria—a partnership that promises to deliver reliable, efficient, and future-ready land management solutions.