In a world increasingly driven by data, location is becoming one of the most powerful dimensions of insight, and at the heart of that insight lies Geographic Information Systems (GIS). The GIS field is evolving rapidly, transforming from traditional mapping into a dynamic and high-demand career path intersecting with data science, artificial intelligence, urban development, and environmental management.
Whether you’re a student, a professional seeking to upskill, or someone curious about the future of location intelligence, this blog post will guide you through the critical skills you need to stay competitive in the GIS field today and tomorrow.

The Evolving GIS Landscape
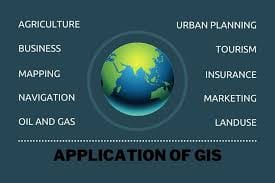
Over the past decade, GIS has expanded beyond cartography and urban planning into nearly every major sector: agriculture, public health, transportation, logistics, climate science, and retail. As organizations recognize the value of spatial data for decision-making, the demand for GIS talent has soared.
With the rise of smart cities, drone mapping, real-time tracking systems, and location-aware apps, GIS professionals now work at the crossroads of technology, geography, and data analytics. And with this evolution comes a shift in the skillsets required to thrive in the field.
Core GIS Skills Every Professional Still Needs
Despite technological advancement, there are foundational GIS skills that remain essential:
- Spatial Analysis & Cartography: Understanding spatial relationships, creating meaningful maps, and conducting geostatistical analysis is still the core of GIS work.
- GIS Software Proficiency: Tools like ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo are still industry standards. A strong command of these platforms is critical for both technical and analytical tasks.
- Coordinate Systems and Projections: Misunderstanding spatial reference systems can lead to inaccurate data interpretation. Knowing how to manage projections ensures spatial accuracy.
- Data Collection & Field Mapping: Skills in GPS data collection and mobile GIS tools remain vital for environmental studies, land surveys, and infrastructure projects.
These basics create a strong foundation. But to future-proof your GIS career, you need to build beyond them.
Emerging & In-Demand Skills to Learn Now
To stay ahead in the GIS job market, you must embrace new technologies and develop hybrid skills that blend geospatial knowledge with broader tech fluency.
- Programming & Automation
Python and R are increasingly used for geoprocessing, data analysis, and automation.Learn to write scripts for automating repetitive tasks, managing spatial data, and building custom GIS tools, JavaScript is essential if you want to work in web-based GIS applications.
- Web GIS & Development
Modern GIS is moving to the web. Skills in ArcGIS Online, Mapbox, Leaflet.js, and OpenLayers help professionals create interactive, shareable maps. Knowing how to develop and maintain GIS dashboards, story maps, and spatial web apps is a huge asset.
- Remote Sensing & Drone Data
With satellite imagery and drones becoming more accessible, learning remote sensing techniques and tools like ENVI and Google Earth Engine is valuable. GIS professionals with drone piloting certifications and image analysis skills are especially sought after in agriculture, mining, and environmental fields.
- Database & Cloud GIS
Learn SQL and spatial databases like PostgreSQL/PostGIS to manage large geospatial datasets. Understanding cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) and services like ArcGIS Enterprise can make you indispensable in large organizations.
- 3D GIS & Visualization
Visualization is moving into 3D and even VR/AR. Tools like Esri CityEngine, Unity, or Blender help create immersive spatial experiences. 3D GIS is particularly relevant for city planning, real estate, and architecture.
- AI & Machine Learning in GIS
GIS is now converging with AI/ML for predictive modeling, image classification, and anomaly detection. Learn how to apply machine learning algorithms to spatial data using Python or cloud-based platforms.
Soft Skills That Set You Apart
GIS is not just about technical skills. Employers are also looking for professionals who can work well in teams, manage projects, and communicate insights effectively.
- Problem-Solving & Critical Thinking: Every GIS project starts with a spatial question. The ability to translate real-world problems into spatial analyses is key.
- Data Storytelling: You must be able to present maps and analysis in a compelling way to non-technical stakeholders.
- Project Management: Managing timelines, stakeholders, and outcomes is important, especially in multi-disciplinary teams.
- Adaptability: GIS roles are found in very different industries. Being flexible and curious allows you to apply your skills in various contexts.
Certifications and Courses to Boost Your GIS Career
Certifications validate your expertise and give you an edge in competitive job markets. Some great options include:
- Esri Technical Certifications – Industry-recognized and platform-specific.
- GISP (Certified GIS Professional) – A broader, experience-based certification.
- Remote Sensing Certification (USGIF or online platforms).
- Courses on Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning. Look for ones focused on:
- Python for GIS
- Spatial Data Science
- Web Mapping with JavaScript
- Google Earth Engine
- Drone Mapping
Career Opportunities & Where to Look
- GIS careers are no longer limited to government agencies. Today, GIS professionals are in demand across:
- Urban Planning & Smart Cities
- Environmental Conservation
- Logistics & Supply Chain Management
- Telecommunications & Utilities
- Healthcare & Epidemiology
- Agritech & Precision Farming
- Retail Site Selection
- Military & Defense