Integrated Workflow
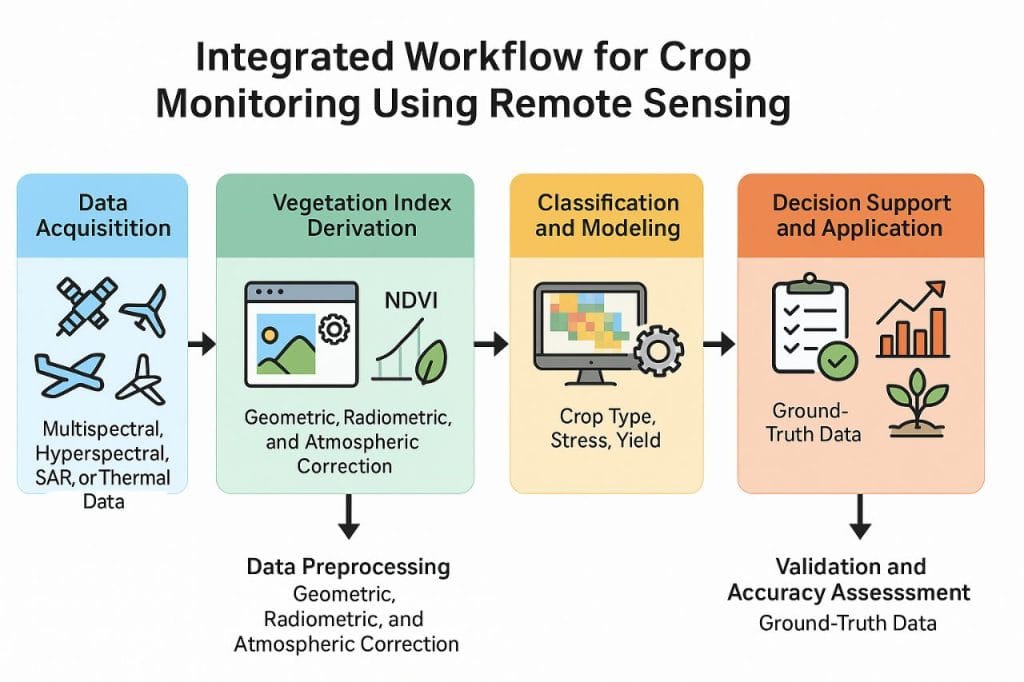
Crop monitoring through remote sensing follows a structured workflow that transforms raw imagery into actionable agricultural intelligence. The process are firmly summarised as follows:
- Data Acquisition: Multispectral, hyperspectral, SAR, or thermal data are collected from satellite, aerial, or UAV platforms covering the target agricultural area.
- Data Preprocessing: The acquired imagery undergoes geometric, radiometric, and atmospheric correction to remove distortions and standardize reflectance values for accurate analysis.
- Vegetation Index Derivation: Key vegetation indices (NDVI, EVI, SAVI, NDWI, etc.) are computed from processed imagery to quantify vegetation vigor, chlorophyll content, and water status.
- Classification and Modelling: Machine learning or statistical models are applied to classify crop types, map growth stages, detect stress, and estimate yield.
- Validation and Accuracy Assessment: Remotely sensed results are validated using ground-truth data collected from field observations, ensuring data reliability and accuracy.
- Decision Support and Application: Final outputs such as health maps, yield forecasts, and stress indicators which are integrated into Decision Support Systems (DSS) for precision irrigation, fertilizer application, pest control, and harvest planning.
Thus, the workflow forms a continuous cycle of data acquisition, processing, analysis, validation, decision-making, and ensuring a dynamic and adaptive monitoring system for sustainable agricultural management.
Applications of Remote Sensing in Crop Monitoring
- Crop type and acreage mapping for agricultural planning.
- Yield forecasting for market and food security assessments.
- Irrigation scheduling based on soil moisture estimates.
- Drought and flood impact analysis on farmlands.
- Pest and disease detection through spectral change detection.
- Precision agriculture—optimizing fertilizer and pesticide use.
- Climate adaptation and resource management through temporal monitoring.
Advantages of Remote Sensing in Agriculture
- Wide and repetitive spatial coverage.
- Non-destructive and cost-effective monitoring.
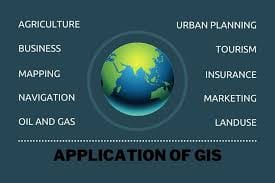
- Integration with GIS for spatial analysis and visualization.
- Early detection of stress and anomalies.
- Enhances decision-making for sustainable farm management.
- Supports national agricultural policies and global food security programs.
Limitations and Challenges
- Cloud interference in optical data acquisition.
- High cost of high-resolution imagery or UAV operations.
- Requirement for technical expertise in data processing.
- Dependence on calibration and ground validation.
- Limited access to advanced technology among smallholder farmers.
Nevertheless, open-access datasets (e.g., Landsat, Sentinel) and cloud-based processing platforms like Google Earth Engine are reducing these barriers, making remote sensing increasingly accessible.
Integration with Emerging Technologies
The effectiveness of remote sensing in crop monitoring is enhanced through integration with other technologies:
- GIS: Spatial mapping and analysis.
- GPS: Accurate field geolocation and data collection.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Real-time soil and environmental sensing.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML): Predictive analytics for yield and stress modeling.
- Cloud Computing: Scalable data storage and processing for large agricultural datasets.
Such integration supports precision agriculture, enabling data-driven management for efficiency, sustainability, and profitability.
Conclusion
The integrated workflow, applications of remote sensing in crop monitoring, advantages of remote sensing in agriculture, limitations and challenges and integration with emerging technologies are key information needed in geospatial study in agriculture.
Contact Geoinfotech Resources Ltd today for drone application on your farm works to receive optimum and satisfactory services. We are competent and confident in serving you with our resources and experience. Geoinfotech Resources Limited is a surveying and GIS company that is well equipped for rendering services in different sectors including agriculture, land survey, environmental monitoring, oil and gas survey/inspection, education, estate planning and management, construction, engineering etc.